两个链表的第一个公共结点
题目:输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点。
链表结点定义
/**
* 链表结点类
*/
private static class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
public ListNode() {
}
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return val + "";
}
}解题思路:
第一种:直接法
在第一个链表上顺序遍历每个结点,每遍历到一个结点的时候,在第二个链表上顺序遍历每个结点。如果在第二个链表上有一个结点和第一个链表上的结点一样,说明两个链表在这个结点上重合,于是就找到了它们的公共结点。如果第一个链表的长度为 m,第二个链表的长度为 n,显然该方法的时间复杂度是 O(mn)。
第二种:使用栈
所以两个有公共结点而部分重舍的链衰,拓扑形状看起来像一个 Y, 而不可能像 X(如图 5.3 所示)。
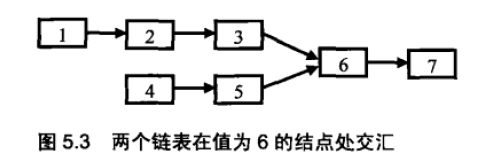
经过分析我们发现,如果两个链表有公共结点,那么公共结点出现在两个链表的尾部。如果我们从两个链衰的尾部开始往前比较,最后一个相同的结点就是我们要找的结点。
在上述思路中,我们需要用两个辅助钱。如果链表的长度分别为 m 和 n,那么空间复杂度是 O(m+n)。这种思路的时间复杂度也是 O(m+n)。和最开始的蛮力法相比,时间效率得到了提高,相当于是用空间消耗换取了时间效率。
第三种:先行法
在图 5.3 的两个链表中,我们可以先遍历一次得到它们的长度分别为 5 和 4, 也就是较长的链表与较短的链表相比多一个结点。第二次先在长的链表上走 1 步,到达结点 2。接下来分别从结点 2 和结点 4 出发同时遍历两个结点, 直到找到它们第一个相同的结点 6,这就是我们想要的结果。
第三种思路和第二种思路相比,时间复杂度都是 O(m+n), 但我们不再需要辅助的拢,因此提高了空间效率。
本题采用第三种解法。
代码实现
public class Test37 {
/**
* 链表结点类
*/
private static class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
public ListNode() {
}
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return val + "";
}
}
/**
* 找两个结点的第一个公共结点,如果没有找到返回null,方法比较好,考虑了两个链表中有null的情况
*
* @param head1 第一个链表
* @param head2 第二个链表
* @return 找到的公共结点,没有返回null
*/
public static ListNode findFirstCommonNode(ListNode head1, ListNode head2) {
int length1 = getListLength(head1);
int length2 = getListLength(head2);
int diff = length1 - length2;
ListNode longListHead = head1;
ListNode shortListHead = head2;
if (diff < 0) {
longListHead = head2;
shortListHead = head1;
diff = length2 - length1;
}
for (int i = 0; i < diff; i++) {
longListHead = longListHead.next;
}
while (longListHead != null && shortListHead != null && longListHead != shortListHead) {
longListHead = longListHead.next;
shortListHead = shortListHead.next;
}
// 返回第一个相同的公共结点,如果没有返回null
return longListHead;
}
private static int getListLength(ListNode head) {
int result = 0;
while (head != null) {
result++;
head = head.next;
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
test1();
test2();
test3();
test4();
}
private static void test1() {
// 第一个公共结点在链表中间
// 1 - 2 - 3 \
// 6 - 7
// 4 - 5 /
ListNode n1 = new ListNode(1);
ListNode n2 = new ListNode(2);
ListNode n3 = new ListNode(3);
ListNode n4 = new ListNode(4);
ListNode n5 = new ListNode(5);
ListNode n6 = new ListNode(6);
ListNode n7 = new ListNode(7);
n1.next = n2;
n2.next = n3;
n3.next = n6;
n6.next = n7;
n4.next = n5;
n5.next = n6;
System.out.println(findFirstCommonNode(n1, n4)); // 6
}
private static void test2() {
// 没有公共结点
// 1 - 2 - 3 - 4
//
// 5 - 6 - 7
ListNode n1 = new ListNode(1);
ListNode n2 = new ListNode(2);
ListNode n3 = new ListNode(3);
ListNode n4 = new ListNode(4);
ListNode n5 = new ListNode(5);
ListNode n6 = new ListNode(6);
ListNode n7 = new ListNode(7);
n1.next = n2;
n2.next = n3;
n3.next = n4;
n5.next = n6;
n6.next = n7;
System.out.println(findFirstCommonNode(n1, n5)); // null
}
private static void test3() {
// 公共结点是最后一个结点
// 1 - 2 - 3 - 4 \
// 7
// 5 - 6 /
ListNode n1 = new ListNode(1);
ListNode n2 = new ListNode(2);
ListNode n3 = new ListNode(3);
ListNode n4 = new ListNode(4);
ListNode n5 = new ListNode(5);
ListNode n6 = new ListNode(6);
ListNode n7 = new ListNode(7);
n1.next = n2;
n2.next = n3;
n3.next = n4;
n4.next = n7;
n5.next = n6;
n6.next = n7;
System.out.println(findFirstCommonNode(n1, n5)); // 7
}
private static void test4() {
// 公共结点是第一个结点
// 1 - 2 - 3 - 4 - 5
// 两个链表完全重合
ListNode n1 = new ListNode(1);
ListNode n2 = new ListNode(2);
ListNode n3 = new ListNode(3);
ListNode n4 = new ListNode(4);
ListNode n5 = new ListNode(5);
ListNode n6 = new ListNode(6);
ListNode n7 = new ListNode(7);
n1.next = n2;
n2.next = n3;
n3.next = n4;
n4.next = n5;
System.out.println(findFirstCommonNode(n1, n1)); // 1
}
}运行结果
上一篇: 数组中的逆序对
下一篇: 数字在排序数组中...