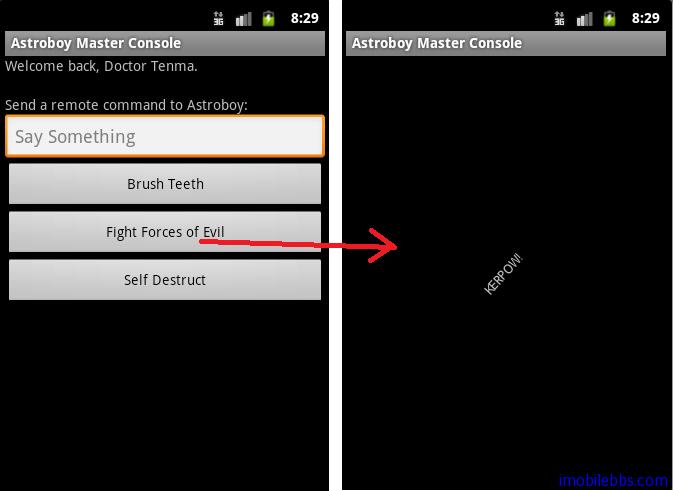
綜合示例 Astroboy
前面介紹了 RogoGuice2.0 的基本用法,其它使用可以參見 RoboGuice1.1 開發指南,2.0中提供了對 Fragment,View(自定義View 中使用注入)的支持,本博客不再一一介紹。
本例使用的是 RoboGuice 開發包中的簡單示例 Astroboy (阿童木)。涉及的使用 RoboGuice2.0 的一些常用方法。
下面對項目中 RoboGuice2 的使用進行解釋。因為本例沒使用自定義綁定,所以無需使用 res/values/roboguice.xml 定義 Module. 如有自定義模塊,可以參見 Android RoboGuice2 使用指南(2): 第一個例子 Hello World。
- 類 Astroboy
// There's only one Astroboy, so make it a @Singleton.
// This means that there will be only one instance of Astroboy in the entire
// app.
// Any class that requires an instance of Astroboy will get the same instance.
// This also means this class needs to be thread safe, of course
@Singleton
public class Astroboy {
// Because Astroboy is a Singleton, we can't directly inject the current
// Context since the current context may change depending on what activity
// is using Astroboy
// at the time. Instead we use the application context.
// Vibrator is bound to context.getSystemService(VIBRATOR_SERVICE) in
// DefaultRoboModule.
// Random has no special bindings, so Guice will create a new instance for
// us.
@Inject Application application;
@Inject Vibrator vibrator;
@Inject Random random;
public void say(String something) {
// Make a Toast, using the current context as returned by the Context
// Provider
Toast.makeText(application, "Astroboy says, \"" + something + "\"",
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
public void brushTeeth() {
vibrator.vibrate(
new long[] { 0, 200, 50, 200, 50, 200, 50, 200, 50, 200, 50,
200, 50, 200, 50, 200, 50, 200, 50, 200, 50, 200, 50, },
-1);
}
public String punch() {
final String expletives[] = new String[] { "POW!", "BANG!", "KERPOW!",
"OOF!" };
return expletives[random.nextInt(expletives.length)];
}
}
程序中只希望使用一個 Astroboy 實例,因此可以使用 @Singleton 標註,此後任何使用
@Inject Astroboy astroboy;
注入的 Astroboy 都會指向同一個實例,這也是符合 Singleton 設計模式的。
@Inject Application application; 注入 Application 實例。參見Android RoboGuice 使用指南(15):Inject Context
@Inject Vibrator vibrator; 注入 Android Vibrator 實例,參見Android RoboGuice 使用指南(16):Standard Injection
@Inject Random random; 對於普通的 Java 類型(POJO),如果該類具有 預設構造函數(不帶參數的等),也可以使用 RoboGuice 自動注入實例。
因此當 Astroboy 創建時,RoboGuice 自動為 application, vibrator, random 創建實例,無需使用 new 或參數傳入來構造它們。
- 類 AstroboyRemoteControl
/**
* A class to control Astroboy remotely.
*
* This class uses the current context, so we must make it @ContextSingleton.
* This means that there will be one AstroboyRemoteControl for every activity or
* service that requires one. Note that we actually ask for the Activity, rather
* than the Context (which is the same thing), because we need access to some
* activity-related methods and this saves us from having to downcast to an
* Activity manually.
*
* It also asks RoboGuice to inject the Astroboy instance so we can control him.
*
* What you'll learn in this class - What @ContextScope means and when to use it
* - How to inject an Activity instead of a Context (which is really the same
* thing) - How to use RoboGuice's convenient and flexible logging facility, Ln.
*/
@ContextSingleton
public class AstroboyRemoteControl {
// The Astroboy class has been decorated with @Singleton, so this instance
// of Astroboy will be the same instance used elsewhere in our app.
// Injecting an Activity is basically equivalent to "@Inject Context context",
// and thus also requires @ContextScope. If you wanted, you could also
// @Inject Application, Service, etc. wherever appropriate.
@Inject Astroboy astroboy;
@Inject Activity activity;
public void brushTeeth() {
// More info about logging available here:
// http://code.google.com/p/roboguice/wiki/Logging
Ln.d("Sent brushTeeth command to Astroboy");
astroboy.brushTeeth();
}
public void say(String something) {
Ln.d("Sent say(%s) command to Astroboy", something);
astroboy.say(something);
}
public void selfDestruct() {
Toast.makeText(
activity,
"Your evil remote control has exploded! Now Astroboy is FREEEEEEEEEE!",
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
activity.finish();
}
}
與 Singleton 類似的一個 Scope 標註為 @ContextSingleton ,它表示對於每個 Activity 實例有一個實例,不同的 activity 對應不同的實例。
@Inject Astroboy astroboy; 注入同一個 Astroboy 實例(Singleton)。
@Inject Astroboy astroboy; 注入對應的 Activity 實例。
- 類 AstroboyMasterConsole
/**
* This activity uses an AstroboyRemoteControl to control Astroboy remotely!
*
* What you'll learn in this class: - How to use @InjectView as a typesafe
* version of findViewById() - How to inject plain old java objects as well
* (POJOs) - When injection happens - Some basics about injection, including
* when injection results in a call to an object's default constructor, versus
* when it does something "special" like call getSystemService()
*/
@ContentView(R.layout.main)
public class AstroboyMasterConsole extends RoboActivity {
// Various views that we inject into the activity.
// Equivalent to calling findViewById() in your onCreate(), except more
// succinct
@InjectView(R.id.self_destruct) Button selfDestructButton;
@InjectView(R.id.say_text) EditText sayText;
@InjectView(R.id.brush_teeth) Button brushTeethButton;
@InjectView(tag = "fightevil") Button fightEvilButton; // we can also use tags if we want
// Standard Guice injection of Plain Old Java Objects (POJOs)
// Guice will find or create the appropriate instance of AstroboyRemoteControl for us
// Since we haven't specified a special binding for AstroboyRemoteControl,
// Guice will create a new instance for us using AstroboyRemoteControl's default constructor.
// Contrast this with Vibrator, which is an Android service that is
// pre-bound by RoboGuice.
// Injecting a Vibrator will return a new instance of a Vibrator obtained by
// calling
// context.getSystemService(VIBRATOR_SERVICE). This is configured in
// DefaultRoboModule, which is
// used by default to configure every RoboGuice injector.
@Inject AstroboyRemoteControl remoteControl;
@Inject Vibrator vibrator;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); // @Inject, @InjectResource, and
// @InjectExtra injection happens
// during super.onCreate()
sayText.setOnEditorActionListener(new OnEditorActionListener() {
public boolean onEditorAction(TextView textView, int i,
KeyEvent keyEvent) {
// Have the remoteControl tell Astroboy to say something
remoteControl.say(textView.getText().toString());
textView.setText(null);
return true;
}
});
brushTeethButton.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(View view) {
remoteControl.brushTeeth();
}
});
selfDestructButton.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(View view) {
// Self destruct the remoteControl
vibrator.vibrate(2000);
remoteControl.selfDestruct();
}
});
// Fighting the forces of evil deserves its own activity
fightEvilButton.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(View view) {
startActivity(new Intent(AstroboyMasterConsole.this,
FightForcesOfEvilActivity.class));
}
});
}
}
AstroboyMasterConsole 為主Activity,要使用RoboGuice,則Activity需從RoboActivity派生,其它如Service,Fragment等可以參見Android RoboGuice 使用指南(13):RoboGuice 功能描述。
@InjectView(R.id.self_destruct) Button selfDestructButton; 注入View實例,功能同findViewById。 它的另外一種方法是使用Tag,如
@InjectView(tag = “fightevil”) Button fightEvilButton ,功能一樣。
這個類使用@ContentView(R.layout.main) 為Activity指明ContentView,無需再調用setContentView.
4. 類FightForcesOfEvilActivity
/**
* Things you'll learn in this class: - How to inject Resources - How to use
* RoboAsyncTask to do background tasks with injection - What it means to be a @Singleton
*/
public class FightForcesOfEvilActivity extends RoboActivity {
@InjectView(R.id.expletive) TextView expletiveText;
// You can also inject resources such as Strings, Drawables, and Animations
@InjectResource(R.anim.expletive_animation) Animation expletiveAnimation;
// AstroboyRemoteControl is annotated as @ContextSingleton, so the instance
// we get in FightForcesOfEvilActivity will be a different instance than
// the one we got in AstroboyMasterConsole
// @Inject AstroboyRemoteControl remoteControl;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.fight_evil);
expletiveText.setAnimation(expletiveAnimation);
expletiveAnimation.start();
// Throw some punches
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
new AsyncPunch(this) {
@Override
protected void onSuccess(String expletive) throws Exception {
expletiveText.setText(expletive);
}
// We could also override onException() and onFinally() if we
// wanted
}.execute();
}
// This class will call Astroboy.punch() in the background
public static class AsyncPunch extends RoboAsyncTask<String> {
// Because Astroboy is a @Singleton, this will be the same
// instance that we inject elsewhere in our app.
// Random of course will be a new instance of java.util.Random, since
// we haven't specified any special binding instructions anywhere
@Inject Astroboy astroboy;
@Inject Random random;
public AsyncPunch(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public String call() throws Exception {
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(5 * 1000));
return astroboy.punch();
}
}
}
@InjectResource(R.anim.expletive_animation) Animation expletiveAnimation; 注入資源,可以參見 Android RoboGuice 使用指南(18):Inject Resources。
從代碼中可以看出使用 RoboGuice 注入可以簡化程序,運行結果如下圖: