Binding Annotations
有些情况需要将同一类型映射到不同的类实现,还是使用绘图的例子.
IShape, Rectangle, MyRectangle, MySquare, 有如下继承关系:
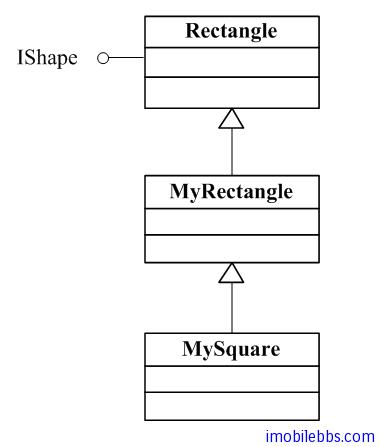
我们可能需要将 IShape 同时映射到 MyRectangle 和 MySquare ,这时可以使用 Binding Annotation 来实现。 这时使用类型和 annotation (标注)可以唯一确定一个 Binding。Type 和 annotation 对称为 Key(键)。
为了同时使用 MyRectangle 和 MySequare,我们定义两个 annotation,如下
import com.google.inject.BindingAnnotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import static java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME;
import static java.lang.annotation.ElementType.PARAMETER;
import static java.lang.annotation.ElementType.FIELD;
import static java.lang.annotation.ElementType.METHOD;
...
@BindingAnnotation
@Target({ FIELD, PARAMETER, METHOD })
@Retention(RUNTIME)
public @interface Rectangle {
}
...
@BindingAnnotation
@Target({ FIELD, PARAMETER, METHOD })
@Retention(RUNTIME)
public @interface Square {
}定义了两个标注 @Rectangle, @Square, 至于 @BindingAnnotation,@Target,@Retention 你并不需要详细了解,有兴趣的可以参见 Java Annotation tutorial
简单的说明如下:
- @BindingAnnotation 通知这是一个 Binding Annotation,如果将多个个标注应用到同一个元素时,Guice 会报错。
- @Target({FIELD, PARAMETER, METHOD}) 表示这个标注可以应用到类成员变量,函数的参数或时方法。
- @Retention(RUNTIME) 表示这个标注在程序运行时可以使用 Reflection 读取。
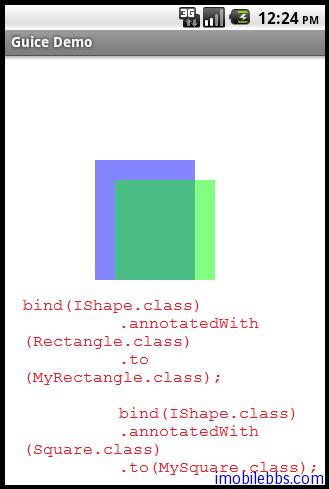
创建一个 BindingAnnotationsDemo 用来绘制两个图形:
public class BindingAnnotationsDemo extends Graphics2DActivity{
@Inject @Rectangle IShape shape1;
@Inject @Square IShape shape2;
protected void drawImage(){
/**
* The semi-opaque blue color in
* the ARGB space (alpha is 0x78)
*/
Color blueColor = new Color(0x780000ff,true);
/**
* The semi-opaque green color in the ARGB space (alpha is 0x78)
*/
Color greenColor = new Color(0x7800ff00,true);
graphics2D.clear(Color.WHITE);
graphics2D.Reset();
SolidBrush brush=new SolidBrush(blueColor);
graphics2D.fill(brush,shape1);
AffineTransform at = new AffineTransform();
at.translate(20, 20);
graphics2D.setAffineTransform(at);
brush=new SolidBrush(greenColor);
graphics2D.fill(brush,shape2);
}
}使用标注将 shape1 绑定到 MyRectangle, shape2 绑定到 MySquare,对应的 Module 定义如下:
public class Graphics2DModule extends AbstractAndroidModule{
@Override
protected void configure() {
bind(IShape.class)
.annotatedWith(Rectangle.class)
.to(MyRectangle.class);
bind(IShape.class)
.annotatedWith(Square.class)
.to(MySquare.class);
}
}
Inject 可以应用到 Field (成员变量),Parameter (参数)或 Method (方法),前面的例子都是应用到 Field 上,如果应用到参数可以有如下形式:
@Inject
public IShape getShape(@Rectangle IShape shape){
...
}如果你不想自定义 Annotation,可以使用 Guice 自带的 @Name 标注来解决同一类型绑定到不同实现的问题。
修改上面代码:
//@Inject @Rectangle IShape shape1;
//@Inject @Square IShape shape2;
@Inject @Named("Rectangle") IShape shape1;
@Inject @Named("Square") IShape shape2;修改绑定如下:
//bind(IShape.class)
//.annotatedWith(Rectangle.class)
//.to(MyRectangle.class);
//bind(IShape.class)
//.annotatedWith(Square.class)
//.to(MySquare.class);
bind(IShape.class)
.annotatedWith(Names.named("Rectangle"))
.to(MyRectangle.class);
bind(IShape.class)
.annotatedWith(Names.named("Square"))
.to(MySquare.class);这种方法简单,但编译器无法检测字符串,比如将 ”Square” 错写为 ”Sqare”,编译器无法查出这个错误,此时到运行时才可能发现 shape2 无法注入,因此建议尽量少用 Named.