调整集群的分片分配
在ElasticSearch Server一书中,我们探讨了如何强制改变分片的分配方式,如何取消、如何使用一条API命令在集群中转移分片。然而在谈论到分片分配时,ElasticSearch允许我们做的不止如此,我们还可以定义以系列用于分片分配的规则。例如,假定一个4-节点的集群,图示如下:

Allocation awareness 配置
Allocation awareness制允许用户使用泛型参数来配置分片及分片副本的分配。为了演示allocation awareness的工作方式,我们使用我们的样例集群。为了集群的演示效果,我们在elasticsearch.yml文件中添加如下的属性:cluster.routing.allocation.awareness.attributes:group
这条配置命令用来通知Elasticsearh使用node.group属性作为集群的awareness参数。


设置cluster.routing.allocation.awareness.attributes属性的参数时,可以指定多个值。比如: cluster.routing.allocation.awareness.attributes:group,node
参数设置好以后,我们先启动两个节点,两个节点的node.group值都是groupA,并且用如下的命令创建索引:
curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/mastering' -d '{
"settings" : {
"index" : {
"number_of_shards" : 2,
"number_of_replicas" : 1
}
}
}'
这个命令执行后,我们的2-节点集群看起来或多或少地类似于下面的图形:
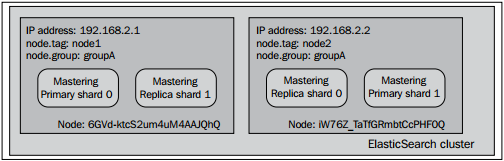
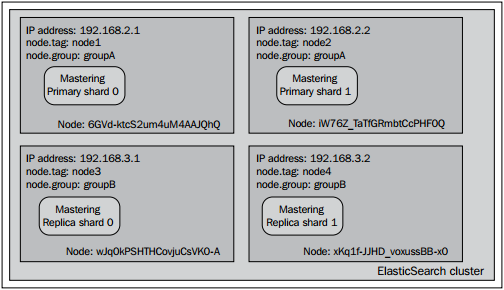
注意两者的不同点:主分片并没有从原来分配的节点中移出,反而是分片副本移动到了node.grooup值不同的节点中,这正是我们所希望的结果。在集群中使用了shard allocation awareness功能后,ElasticSearch不会把决定allocation awareness的属性(在本例中是node.group值)相同的分片或者分片副本分配到同一个节点中。该功能典型的用例是把集群拓扑结构部署到物理机或者虚拟机时,确保你的集群不会出现单点故障问题。


请记住在使用allocation awareness功能时,分片不会被分配到没有设置相应属性的节点上。所在在我们的案例中,分片分配机制不会考虑分配分片到没有设置node.group属性的节点。
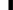
Forcing allocation awareness
(文本的描述不并清晰,参考http://www.elasticsearch.org/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/modules-cluster.html,一看就懂) 当我们事先知道awareness属性的取值范围并且不希望集群中有过多的分片副本时,使用forcing allocation awareness机制会很方便。比如,不希望集群中负载了过多的分片副本,我们可以强制allocation awareness只在有确定参数值时起作用。我们可以指定cluster.routing.allocation.awareness.force.zone.values属性的值,这是一个多值属性,多个值可以用逗号区分开来。比如,如果我们希望allocation awareness只在node.group属性的值为groupA和groupB生效时,我们可以在elasticsearch.yml文件中加入如下的代码:
cluster.routing.allocation.awareness.attributes: group
cluster.routing.allocation.awareness.force.zone.values: groupA, groupB
过滤
ElasticSearch允许用户从整个集群或者索引的层面上配置allocation机制。在集群层面上配置allocation机制时,我们可以用如下的属性前缀:
- cluster.routing.allocation.include
- cluster.routing.allocation.require
- cluster.routing.allocation.exclude
- index.routing.allocation.include
- index.routing.allocation.require
- index.routing.allocation.exclude
cluster.routing.allocation.include.\_ip:192.168.2.1如果我们希望把group属性值为groupA的节点包括进来,我们可以设置如下的属性:
cluster.routing.allocation.include.group:groupA注意我们使用cluster.routing.allocation.include属性的方式是以它为前缀并和其它属性的名字串联起来,在本例中是group属性。
include,exclude,required属性的意义
如果读者仔细观察了前面提到的参数,应该能注意到它们分为三种:
- include:这种类型将导致所有定义了该参数的节点都会被包括进来。如果配置多种include的条件,那么在进行分片分配的时候,只要有一个条件满足,节点就会被allocation考虑进去。比如,如果我们在配置的cluster.routing.allocation.include.tag参数中中添加2个值:node1和node2,那么最终索引的分片会分配到第一个节点和第二个节点中(从左到右数)。总结一下:对于带有include allocation参数类型的结点,ElasticSearch会考虑把分片分配到该节点,但是并不意味着ElasticSearch一定会把分片分配到节点。
- require:这个属性是ElasticSearch 0.90版本引入到allocation filter中去的。它需要节点的所有相关属性值都满足它设定的值。比如,如果我们往配置文件中添加cluster.routing.allocation.require.tag参数并设其值为node1,添加cluster.routing.allocation.require.group参数并设其值为groupA,最终所有的分片将会分配到第一个节点(IP值为192.168.2.1的节点)
- exclude:这个属性允许我们在allocation过程中排除匹配属性值的节点。比如,如果我们设置cluster.routing.allocation.include.tag的值为groupA,最终我们的索引分片只会分配到IP值为192.168.3.1和192.168.3.2的节点上(例子中的第3和第4个节点)。


属性值可以使用简单的正则表达式。比如,如果我们包含所有group属性中属性值以字符串group开头的结点,可以设置cluster.routing.allocation.include.group的值为group*。在我们的样例集群中,它会匹配到group参数值为groupA和groupB的节点。
运行时allocation参数更新
除了可以在elasticsearch.yml文件中设置前面讨论的属性,当集群在线时,我们也可以通过update API来实时更新这些参数。
索引层面的参数更新
如果想更新给定索引(比如例子中的mastering索引)的配置信息,我们就要运行运行如下的命令:
curl -XPUT 'localhost:9200/mastering/_settings' -d '{
"index.routing.allocation.require.group": "groupA"
}'
正如你所看到的,命令被发送到给定索引的_settings端点。在一条命令中可以包含多个属性。
集群层面的参数更新
如果想更新整个集群的配置信息,我们就要运行运行如下的命令:curl -XPUT 'localhost:9200/_cluster/settings' -d '{
"transient" : {
"cluster.routing.allocation.require.group": "groupA"
}
}'
正如你所看到的,命令被发送到_cluster_settings端点。在一条命令中可以包含多个属性。请记住上面命令中transient关键字,它表示设置的属性在集群重启后就不再生效。如果希望设置的属性永久生效,用persistent属性代替transient属性就可以了。下面的命令示例将会使用用户设置在系统重启后依然生效:
curl -XPUT 'localhost:9200/_cluster/settings' -d '{
"persistent" : {
"cluster.routing.allocation.require.group": "groupA"
}
}'


请注意,在相应的结节上运行上面的命令时,会导致分片在节点间的移动。
限定每个分片上节点的数量
除了前面提到的那些属性,我们也允许用户自定义每个节点上能够分配的分片(主分片和分片副本)数量。为了实现这个功能,用户需要在index.routing.allocation.total\_shards\_per\_node属性中设置相应的值。比如在elasticsearch.yml文件中,我们应该设置如下:index.routing.allocation.total\_shards\_per\_node:4
这个属性规定了每个节点中,单个索引最多允许分配4个分片。这个属性也可以通过update API在线上实时修改:
curl -XPUT 'localhost:9200/mastering/_settings' -d '{
"index.routing.allocation.total_shards_per_node": "4"
}'
现在,让我们看看在elasticsearch.yml文件中配置了allocation的相关属性后,几个单索引集群会变成什么样。
"结点包含"属性
现在通过我们的示例集群来看看allocation inclusion 是怎么工作的。最开始,用如下的命令创建一个mastering索引。curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/mastering' -d '{
"settings" : {
"index" : {
"number_of_shards" : 2,
"number_of_replicas" : 0
}
}
}'
创建索引后,试着执行如下的命令:
curl -XPUT 'localhost:9200/mastering/_settings' -d '{
"index.routing.allocation.include.tag": "node1",
"index.routing.allocation.include.group": "groupA",
"index.routing.allocation.total_shards_per_node": 1
}'
如果让索引状态可视化,那么集群看起来应该跟下面的图差不多.
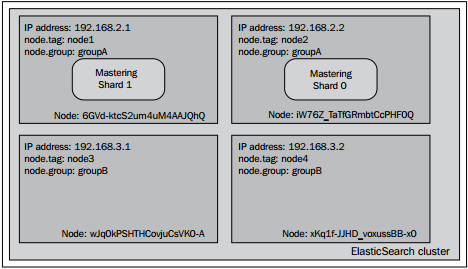
正如你所看见的,Mastering索引的分片只分配到了tag属性值为node1或者group属性值为groupA的节点。
"结点必须"属性
现在对我们的示例集群再回收利用(假定集群中已经没有任何索引存在)。我们再一次用如下的命令创建一个mastering索引:
curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/mastering' -d '{
"settings" : {
"index" : {
"number_of_shards" : 2,
"number_of_replicas" : 0
}
}
}'
随后,试着执行下面命令:
curl -XPUT 'localhost:9200/mastering/_settings' -d '{
"index.routing.allocation.require.tag": "node1",
"index.routing.allocation.require.group": "groupA"
}'
如果让索引状态可视化,那么集应该跟如下图所示:
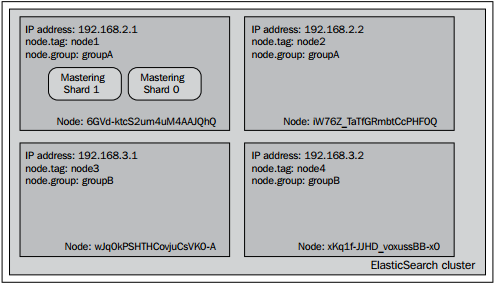
我们可以看到图示跟使用include属性有些不同。这是因为我们告诉ElasticSearch把Mastering索引的分片只分配到满足require参数所有设定值的节点上,在本例中只有第一个节点满足条件。
"结点排除"属性
我们再一次使用示例集群,并且用如下的命令创建mastering索引:
curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/mastering' -d '{
"settings" : {
"index" : {
"number_of_shards" : 2,
"number_of_replicas" : 0
}
}
}'
随后,试着执行下面的命令来测试allocation exclusion属性:
curl -XPUT 'localhost:9200/mastering/_settings' -d '{
"index.routing.allocation.exclude.tag": "node1",
"index.routing.allocation.require.group": "groupA"
}'
接下来,查看集群中各个节点的状态:
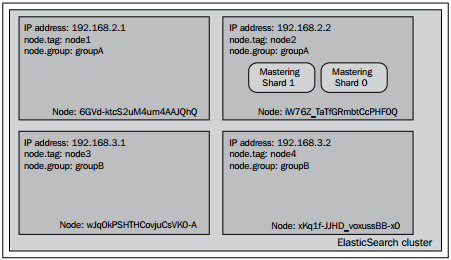
正如所见的那样,我们需要group属性值为groupA,但同时我们又要排除tag属性中值为node1的节点。这导致Mastering索引的分片被分配到了IP地址为192.168.2.2的节点上,这也是我们所希望的。
其它的shard allocation属性
除了前面提到的那些属性,在配置shard allocation时,ElasticSearch还提供了其它的几个特性。下面我们一起来了解一下这些属性,看看集群中还有哪些是我们可以控制的
- cluster.routing.allocation.allow\_rebalance: 这个属性用来控制rebalancing发生的时间,它是基于集群中分片的状态来判断的。这个属性有以下几个可选值:[always,indice\_primaries\_active, indices\_all\_active]。如果设置属性值为always,则rebalancing操作时,不用判断集群中分片的状态。(这个值要小心使用,因为它能导致集群出现高负载状态);如果设置属性值为indice\_primaries\_active,当所有的主分片都可用时,rebalancing才会发生,如果设置属性值为indices\_all\_active,那么必须所有分片(主分片和分片副本)都已经分配就位,rebalancing才会发生。默认值是indices\_all\_active。
- cluster.routing.allocation.cluster\_concurrent\_rebalance:该属性的默认值为2,指定了集群中同一时间允许的rebalance操作的并发数。如果该值设置得比较大,将会导致比较高的I/O,比较频繁的网络活动以及比较高的节点负载。
- cluster.routing.allocation.node\_initial\_primaries\_recoveries:该属性指定了每个节点可以同时恢复的主分片数量。由于主分片的恢复通常比较快,所以就算该值设置得比较高也不会给节点带来太大的压力。该属性的默认值是4。
- cluster.routing.allocation.node\_concurrent\_recoveries:该属性值默认为2。用来指定单节点上恢复操作的并发数。需要记住的是,如果值设置的过大,将到导致非常频繁的I/O活动。
- cluster.routing.allocation.disable\_new\_allocation:该属性值默认为flase。用来禁止新创建的索引分配分片(主分片和分片副本都算在内)。该属性可以用于以下场景:出于某些原因,希望新创建的索引暂时不进行分片的分配。该属性同时也可以用来禁止现有的索引分配新的分片,只需要在该索引中设置index.routing.allocation.disable\_new\_allocation属性的值为true即可。
- cluster.routing.allocation.disable\_allocation:该属性的默认值是false,用来禁止分配已经创建好的分片和分片副本。需要注意把分片副本提升成主分片(在主分片不存在时)操作并不属于分片分配,所以即使该属性值设置为true,对分片提升操作也没有影响。该属性可以用于以下场景:需要短时间禁止新创建的索引进行分片的分配。
- cluster.routing.allocation.disable\_replica\_allocation:该属性值默认为false,如果该属性值设置为true,分片副本的分配将会被禁止。该属性可用于以下场景:需要暂时停止分片副本的分配。该属性也可通过在索引的设置项中设置index.routing.allocation.disable\_replica\_allocation为true来禁止某个特定索引的分片副本的分配。