使用 python 构建基于 hadoop 的 mapreduce 日志分析平台
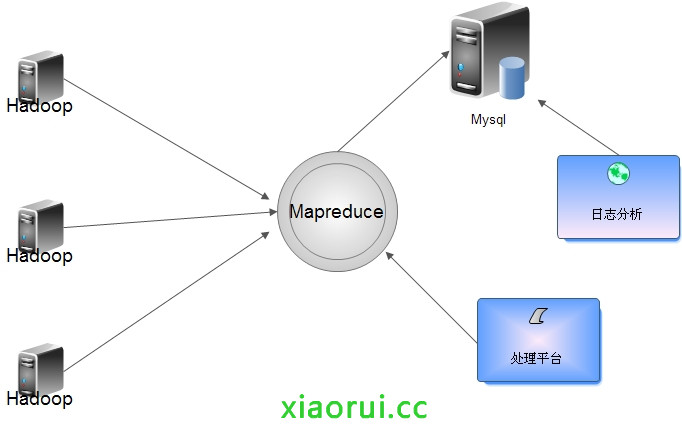
流量比较大的日志要是直接写入 Hadoop 对 Namenode 负载过大,所以入库前合并,可以把各个节点的日志凑并成一个文件写入 HDFS。 根据情况定期合成,写入到 hdfs 里面。
咱们看看日志的大小,200 G 的 dns 日志文件,我压缩到了 18 G,要是用 awk perl 当然也可以,但是处理速度肯定没有分布式那样的给力。
Hadoop Streaming 原理
mapper 和 reducer 会从标准输入中读取用户数据,一行一行处理后发送给标准输出。Streaming 工具会创建 MapReduce 作业,发送给各个 tasktracker,同时监控整个作业的执行过程。
任何语言,只要是方便接收标准输入输出就可以做 mapreduce~
再搞之前我们先简单测试下 shell 模拟 mapreduce 的性能速度~

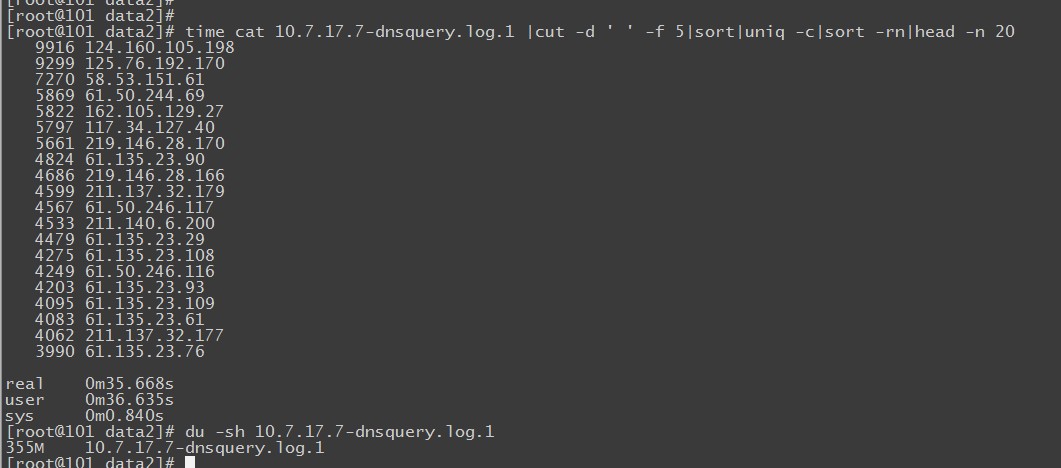
看下他的结果,350 M 的文件用时 35 秒左右。
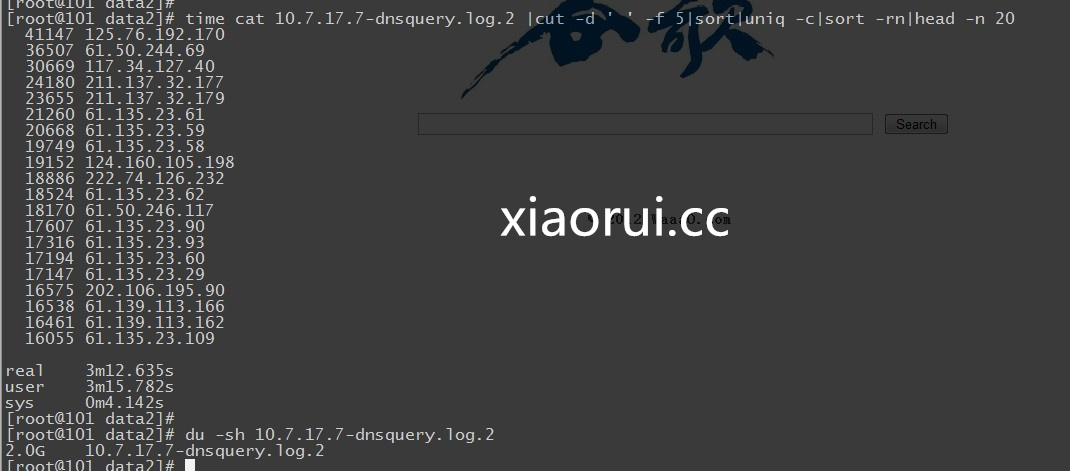
这是 2 G 的日志文件,居然用了 3 分钟。 当然和我写的脚本也有问题,我们是模拟 mapreduce 的方式,而不是调用 shell 下牛逼的 awk,gawk 处理。
awk 的速度!果然很霸道,处理日志的时候,我也很喜欢用 awk,只是学习的难度有点大,不像别的 shell 组件那么灵活简单。

这是官方的提供的两个 demo ~
map.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
"""A more advanced Mapper, using Python iterators and generators."""
import sys
def read_input(file):
for line in file:
# split the line into words
yield line.split()
def main(separator='\t'):
# input comes from STDIN (standard input)
data = read_input(sys.stdin)
for words in data:
# write the results to STDOUT (standard output);
# what we output here will be the input for the
# Reduce step, i.e. the input for reducer.py
#
# tab-delimited; the trivial word count is 1
for word in words:
print '%s%s%d' % (word, separator, 1)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()reduce.py 的修改方式
#!/usr/bin/env python
"""A more advanced Reducer, using Python iterators and generators."""
from itertools import groupby
from operator import itemgetter
import sys
def read_mapper_output(file, separator='\t'):
for line in file:
yield line.rstrip().split(separator, 1)
def main(separator='\t'):
# input comes from STDIN (standard input)
data = read_mapper_output(sys.stdin, separator=separator)
# groupby groups multiple word-count pairs by word,
# and creates an iterator that returns consecutive keys and their group:
# current_word - string containing a word (the key)
# group - iterator yielding all ["<current_word>", "<count>"] items
for current_word, group in groupby(data, itemgetter(0)):
try:
total_count = sum(int(count) for current_word, count in group)
print "%s%s%d" % (current_word, separator, total_count)
except ValueError:
# count was not a number, so silently discard this item
pass
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()咱们再简单点:
#!/usr/bin/env python
import sys
for line in sys.stdin:
line = line.strip()
words = line.split()
for word in words:
print '%s\t%s' % (word, 1)#!/usr/bin/env python
from operator import itemgetter
import sys
current_word = None
current_count = 0
word = None
for line in sys.stdin:
line = line.strip()
word, count = line.split('\t', 1)
try:
count = int(count)
except ValueError:
continue
if current_word == word:
current_count += count
else:
if current_word:
print '%s\t%s' % (current_word, current_count)
current_count = count
current_word = word
if current_word == word:
print '%s\t%s' % (current_word, current_count)咱们就简单模拟下数据,跑个测试
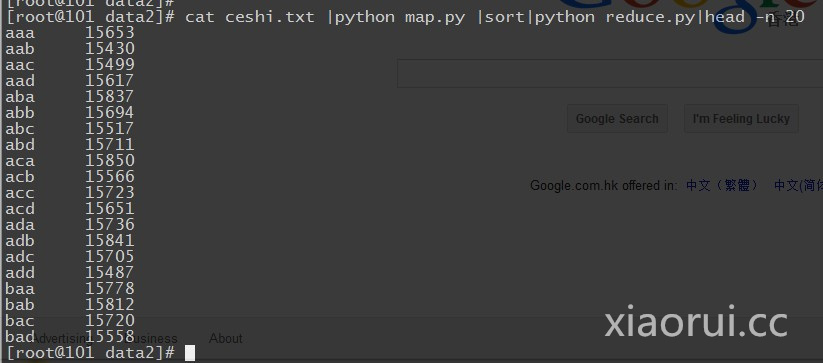
剩下就没啥了,在 hadoop 集群环境下,运行 hadoop 的 steaming.jar 组件,加入 mapreduce 的脚本,指定输出就行了. 下面的例子我用的是 shell 的成分。
[root@101 cron]#$HADOOP_HOME/bin/hadoop jar $HADOOP_HOME/contrib/streaming/hadoop-*-streaming.jar \
-input myInputDirs \
-output myOutputDir \
-mapper cat \
-reducer wc详细的参数,对于咱们来说提供性能可以把 tasks 的任务数增加下,根据情况自己测试下,也别太高了,增加负担。
(1)-input:输入文件路径
(2)-output:输出文件路径
(3)-mapper:用户自己写的 mapper 程序,可以是可执行文件或者脚本
(4)-reducer:用户自己写的 reducer 程序,可以是可执行文件或者脚本
(5)-file:打包文件到提交的作业中,可以是 mapper 或者 reducer 要用的输入文件,如配置文件,字典等。
(6)-partitioner:用户自定义的 partitioner 程序
(7)-combiner:用户自定义的 combiner 程序(必须用 java 实现)
(8)-D:作业的一些属性(以前用的是-jonconf),具体有:
1)mapred.map.tasks:map task 数目
2)mapred.reduce.tasks:reduce task 数目
3)stream.map.input.field.separator/stream.map.output.field.separator: map task 输入/输出数
据的分隔符,默认均为 \t。
4)stream.num.map.output.key.fields:指定 map task 输出记录中 key 所占的域数目
5)stream.reduce.input.field.separator/stream.reduce.output.field.separator:reduce task 输入/输出数据的分隔符,默认均为 \t。
6)stream.num.reduce.output.key.fields:指定 reduce task 输出记录中 key 所占的域数目
这里是统计 dns 的日志文件有多少行 ~
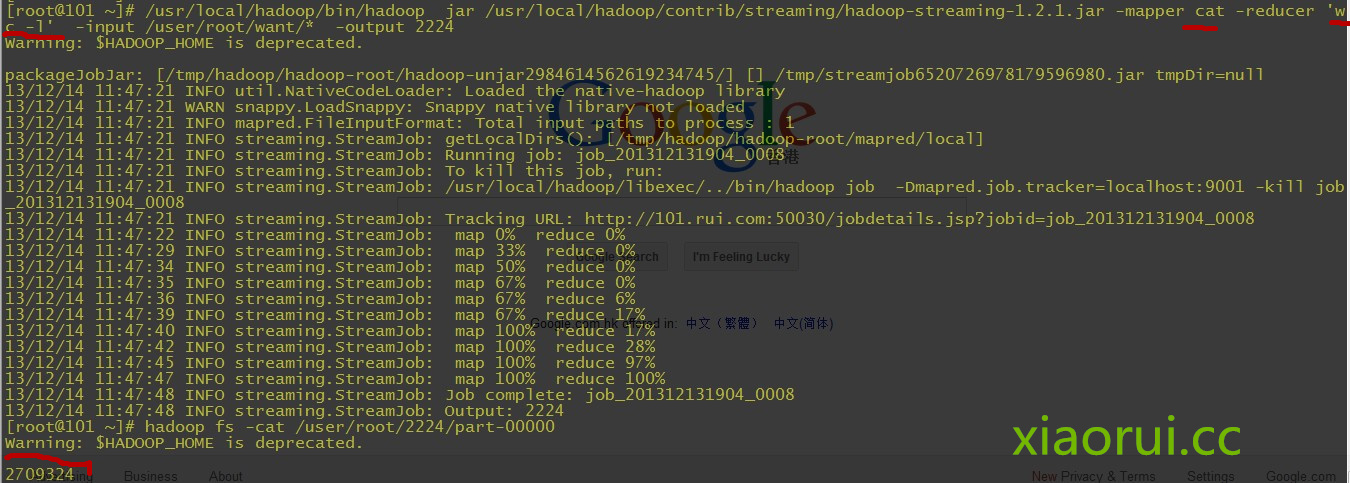
在 mapreduce 作为参数的时候,不能用太多太复杂的 shell 语言,他不懂的~
可以写成 shell 文件的模式;
#! /bin/bash
while read LINE; do
# for word in $LINE
# do
# echo "$word 1"
awk '{print $5}'
done
done#! /bin/bash
count=0
started=0
word=""
while read LINE;do
goodk=`echo $LINE | cut -d ' ' -f 1`
if [ "x" == x"$goodk" ];then
continue
fi
if [ "$word" != "$goodk" ];then
[ $started -ne 0 ] && echo -e "$word\t$count"
word=$goodk
count=1
started=1
else
count=$(( $count + 1 ))
fi
done有时候会出现这样的问题,好好看看自己写的 mapreduce 程序 ~
13/12/14 13:26:52 INFO streaming.StreamJob: Tracking URL: http://101.rui.com:50030/jobdetails.jsp?jobid=job_201312131904_0030
13/12/14 13:26:53 INFO streaming.StreamJob: map 0% reduce 0%
13/12/14 13:27:16 INFO streaming.StreamJob: map 100% reduce 100%
13/12/14 13:27:16 INFO streaming.StreamJob: To kill this job, run:
13/12/14 13:27:16 INFO streaming.StreamJob: /usr/local/hadoop/libexec/../bin/hadoop job -Dmapred.job.tracker=localhost:9001 -kill job_201312131904_0030
13/12/14 13:27:16 INFO streaming.StreamJob: Tracking URL: http://101.rui.com:50030/jobdetails.jsp?jobid=job_201312131904_0030
13/12/14 13:27:16 ERROR streaming.StreamJob: Job not successful. Error: # of failed Map Tasks exceeded allowed limit. FailedCount: 1. LastFailedTask: task_201312131904_0030_m_000000
13/12/14 13:27:16 INFO streaming.StreamJob: killJob...
Streaming Command Failed!python 做为 mapreduce 执行成功后,结果和日志一般是放在你指定的目录下的,结果是在 part-00000 文件里面~
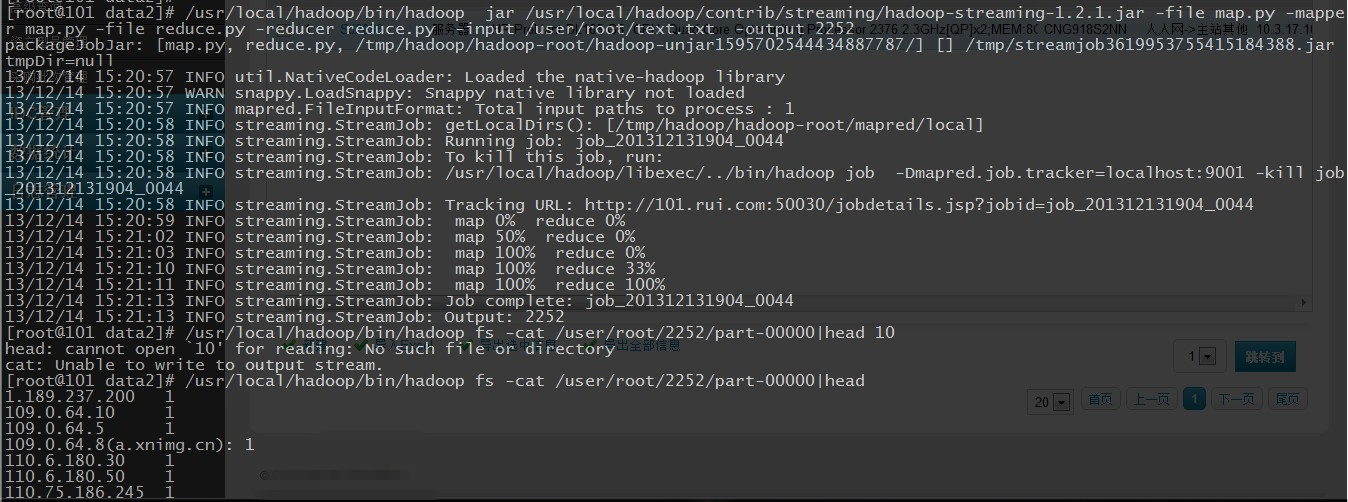
下面咱们谈下,如何入库和后台的执行
本文出自 “峰云,就她了。” 博客,谢绝转载!